What is a Cache Memory? Definition, Example, and Complete Overview
Published: 1 Feb 2025
Cache Memory Explained
Cache memory is a small but super-fast type of memory that speeds up your computer by storing frequently used data. Ever wondered why some apps load instantly while others take time? That’s because cache memory helps your processor access data quickly instead of fetching it from slower RAM. Without it, your system would lag, making multitasking frustrating. Whether you realize it or not, cache memory works silently in the background to keep things running smoothly.
What is Cache Memory?
Cache memory is a compact, fast storage space designed to hold commonly used data for quick retrieval. It enhances your computer’s speed by minimizing the time spent accessing slower memory like RAM, resulting in improved performance, particularly when launching applications or browsing the internet.
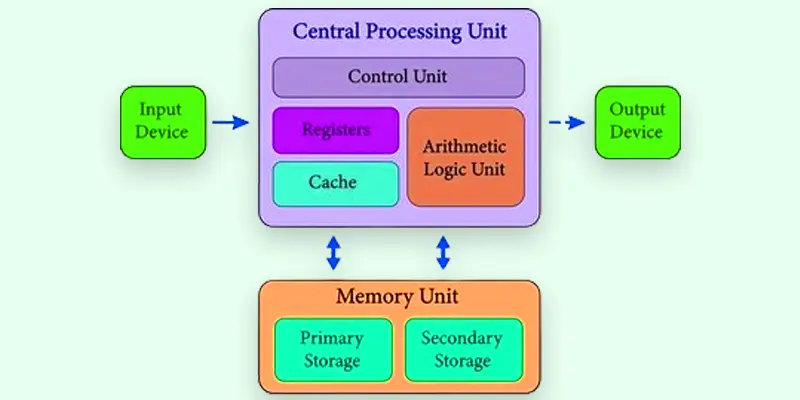
Definition of Cache Memory
Cache memory is a fast, compact storage that keeps frequently used data close to the CPU, allowing for quicker data retrieval. This helps minimize delays and boosts overall system performance.
Example of Cache Memory
- Web Browsers: Store website data to load pages faster.
- CPU Cache: Speeds up data access for quick processing.
- Mobile Apps: Keep recent data for smooth performance.
- Gaming Consoles: Store frequently used game files for faster loading.
- Search Engines: Save past searches to show results quickly.
How Does Cache Memory Work?
- Keeps commonly accessed data ready for fast retrieval.
- The CPU checks the cache before fetching data from RAM.
- If data is found in the cache (cache hit), it loads instantly.
- If data is missing (cache miss), it retrieves it from RAM or storage.
- Helps reduce processing time and improves system speed.
- Works automatically in the background for better performance.
What is the Purpose of Cache Memory?
Its primary role is to store commonly used data, enabling faster access by the CPU and enhancing overall system efficiency and speed. By reducing the need to fetch data from slower memory sources like RAM, cache memory helps the computer run more efficiently, especially during tasks that require fast processing, like gaming or browsing.

Why is Cache Memory Important?
Cache memory plays an important role in boosting data retrieval speed, making your computer operate faster. By holding frequently accessed data, it shortens the time the CPU needs to access slower storage such as RAM. This quick access improves overall system performance and responsiveness.
Without cache memory, the CPU would constantly access slower memory, causing delays and slower load times for apps and files. Cache ensures smoother multitasking, faster app launches, and a better overall user experience.
| Cache Memory | RAM (Random Access Memory) |
|---|---|
| Compact, fast memory for quick access to frequently used data. | Larger memory that holds data and programs currently used by the CPU. |
| Speeds up data retrieval by storing common data. | Temporarily stores data and instructions in use by the CPU. |
| Much faster than RAM. | Slower than cache but faster than hard drive storage. |
| Very small, usually in the range of KB to MB. | Larger, typically ranging from 4GB to 64GB or more. |
| Located inside or very close to the CPU. | Located on the motherboard, separate from the CPU. |
| Extremely fast access time (in nanoseconds). | Slower access time compared to cache memory. |
| CPU cache, L1, L2, L3 caches. | System RAM, DDR4, DDR5. |
| More expensive per unit of memory due to high speed. | Less expensive compared to cache memory. |
| Holds commonly used data and instructions for quick retrieval. | Stores data, instructions, and programs currently in use, and data from running applications. |

Conclusion about Memory Cache
Both cache memory and RAM play vital roles in your computer’s performance, but they serve different purposes. Cache memory is designed to speed up data retrieval by storing frequently used information close to the CPU, while RAM temporarily stores data and programs actively in use. Together, they ensure your system runs smoothly and efficiently. Understanding their differences can help you make better choices when upgrading your hardware.
FAQS – Cache Memory
Cache memory in a processor is a fast, compact storage that keeps commonly used data close to the CPU, allowing for faster access and enhanced processing speed.
Yes, cache memory is considered volatile. It loses its stored data when the power is turned off, similar to other types of RAM.
Yes, cache memory is faster than RAM. It is located closer to the CPU and provides quicker access to frequently used data, improving overall speed.
Clearing the cache can boost speed by removing old or unnecessary data, though it might cause a temporary slowdown as new data is loaded.
Typically, you cannot manually increase the size of cache memory as it is built into the processor, but some systems may allow for hardware upgrades.
No, cache memory is a fast storage used by the CPU for quick access to data, while virtual memory is a system that uses disk space to extend RAM capacity.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks