Disadvantages of Database Management System
Published: 9 Oct 2024
Disadvantages of DBMS in large Organizations
Database Management Systems (DBMS) are powerful tools for storing and managing data efficiently. However, they also have a range of disadvantages that can affect businesses and organizations. These drawbacks can include high costs, complex setups, and the need for specialized staff to manage the system. Understanding these disadvantages is important for anyone considering using a DBMS, as it helps to identify potential challenges and make informed choices about data management.
Disadvantages of DBMS
A Database Management System (DBMS) offers many advantages, but it also comes with several disadvantages.
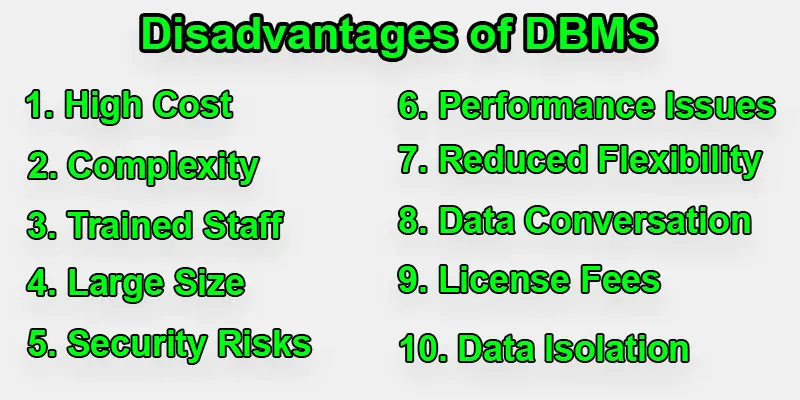
High Cost of Implementing DBMS in Businesses
High cost in a DBMS means that it’s expensive to buy the software, and you often have to pay recurring fees to use it. You also need powerful computers and hardware to run the system, which adds to the cost. Additionally, skilled professionals are required to manage and maintain the DBMS, and their salaries can be high. All of these factors make the overall cost of using a DBMS quite large.
- Software Cost: Software cost in a DBMS refers to the price you pay to buy and use the software. Many DBMS systems require a license, which often comes with recurring fees, not just a one-time payment. These costs can add up, especially for businesses that need advanced features or multiple licenses.
- Hardware Cost: Hardware cost in a DBMS means you need powerful computers and storage devices to run the system smoothly. These devices can be expensive because a DBMS requires a lot of processing power and memory. The better the hardware, the higher the cost.
- Staff Cost: Staff cost in a DBMS refers to the expense of hiring skilled professionals, like database administrators, to manage and maintain the system. These experts are needed to ensure the DBMS runs smoothly, stays secure, and is properly updated. Their salaries can be high, adding to the overall cost of using the system.
- Data Conversation Cost: Data conversion cost refers to the expense involved in moving data from an old system to a new DBMS. This process can be complicated and time-consuming, often requiring special tools or expertise. Because of this, businesses may face additional costs during the transition, making it more expensive to switch to a new system.
Complexity Issues in Database Management Systems
Complexity in a DBMS means that these systems can be difficult to understand and manage, especially for people who are not trained. Setting up the DBMS often involves many steps and technical details, which can be overwhelming. This complexity may lead to mistakes or require extra training for staff, making it harder to use the system effectively. Overall, it can slow down operations and increase the learning curve for new users.
Need for Trained Staff to Manage DBMS
The need for trained staff in a DBMS means you require skilled professionals to manage and maintain the system properly. These experts, like database administrators, know how to handle the technical aspects, ensure security, and troubleshoot issues. Hiring and training these individuals can be expensive and time-consuming. Without the right staff, the DBMS may not function well, leading to potential problems and risks.
Large Size
The large size of a DBMS refers to the significant amount of storage space it requires. Because a DBMS stores a lot of data and files, it can take up a lot of room on servers or computers. This can lead to slower performance if the hardware isn’t powerful enough to handle the load. Managing this large size also means you may need to invest in additional storage solutions, increasing costs and complexity.
Time-Consuming Setup
A time-consuming setup in a DBMS means that installing and configuring the system can take a long time. Setting it up involves multiple steps, like installing software, creating databases, and adjusting settings. This process can be complicated and may require careful planning and testing. Because of this, businesses might experience delays before they can start using the system effectively.
Security Risks in DBMS Systems
Security risks in a DBMS refer to the potential threats that can lead to unauthorized access or data breaches. If the system isn’t properly secured, hackers or malicious users might steal or corrupt important data. Managing security requires constant attention, such as regular updates and monitoring. Failing to address these risks can lead to serious consequences for a business, including loss of trust and financial damage.

Backup and Recovery Challenges in DBMS
Backup and recovery issues in a DBMS refer to the expenses involved in regularly saving data to prevent loss and having a plan to restore it if something goes wrong. Setting up a reliable backup system can require special tools and storage, which adds to the overall cost. Additionally, the process of recovering data after a failure can be complex and time-consuming. These costs are essential to protect valuable information but can strain a budget.
Performance Issues in large | Scale DBMS
Performance issues in a DBMS occur when the system becomes slow or unresponsive, especially when too many users try to access it at the same time. This can lead to delays in retrieving or updating data, which affects productivity. Factors like insufficient hardware or poorly optimized queries can contribute to these problems. When performance suffers, it can frustrate users and impact the overall efficiency of the business.
Continuous Maintenance
Continuous maintenance in a DBMS means that the system requires regular updates and checks to keep it running smoothly. This includes fixing bugs, applying security patches, and optimizing performance. Ongoing maintenance can take a lot of time and resources, as skilled staff are often needed to manage these tasks. If not properly maintained, the DBMS can face issues that affect its reliability and security, leading to potential problems for the business.
Data Conversation
Data conversion in a DBMS involves changing data from an old system to fit the new DBMS format. This process can be complicated and often requires special tools or expertise to ensure everything is transferred correctly. During conversion can lead to data loss or errors, which can be costly to fix. Because of this complexity, businesses may face extra costs and time delays when switching to a new system.
Vendor Dependency
Vendor dependency in a DBMS means that a business relies heavily on one company for its software and support. If the vendor has issues, like price increases or poor service, it can create problems for the business. This dependence can make it difficult to switch to another provider or find alternative solutions. As a result, companies may feel stuck with a vendor, limiting their flexibility and options in the long run.
License Fees
License fees in a DBMS are the costs you pay to use the software legally. These fees are often not just a one-time payment; you may have to pay them regularly, like annually or monthly. If your business needs more features or additional licenses for more users, these costs can quickly add up. This ongoing expense can be a burden for companies, making budgeting for software use more complicated.
Complicated Recovery
Complicated recovery in a DBMS refers to the challenges faced when trying to restore lost or damaged data after a failure. If something goes wrong, like a system crash or data corruption, getting everything back to normal can be tricky and time-consuming. It often requires special tools and expertise, making the process stressful for the team involved. If recovery isn’t done correctly, it can lead to further data loss or issues, adding to the complexity and cost.
Reduced Flexibility
Reduced flexibility in a DBMS means that the system is often rigid and follows strict rules, making it hard to customize. This can limit how businesses can adapt the system to their specific needs or processes. If you want to make changes or add new features, it might be difficult or require significant effort. As a result, companies may feel constrained by the system, making it less suited to their unique requirements.
Data Isolation Problems in Multi | User DBMS
Data isolation in a DBMS means that different pieces of data may be kept separate from each other, making it hard to access related information easily. This can happen when data is stored in different locations or formats. As a result, users might struggle to get a complete picture or find connections between data sets. This separation can complicate analysis and reporting, leading to inefficiencies in how data is used within the organization.
Conclusion About Overall Disadvantages of DBMS for Organizations
While Database Management Systems (DBMS) offer many benefits, they also come with significant disadvantages. High costs, complexity, and the need for trained staff can be challenging for businesses. Additionally, issues like performance problems, security risks, and complicated recovery processes can create further obstacles. Understanding these disadvantages is essential for organizations to make informed decisions about whether a DBMS is the right fit for their needs. By weighing the pros and cons, businesses can better navigate the challenges of using a DBMS effectively.
FAQS – Disadvantages of a Database Management System
The following are some drawbacks of the database system:
- Higher costs: DBMS is more expensive to buy and maintain.
- More complexity: DBMS is harder to set up and manage.
- Need for skilled staff: Requires trained professionals to operate.
- Slower performance: May run slower with many users accessing data.
- Longer setup time: Takes more time to install and configure.
- Complex backups: Backing up data is more complicated.
- Extra processing: This may add unnecessary processing overhead.
A DBMS can be expensive to set up and maintain. It also needs skilled staff to manage it properly.
Common disadvantages include high cost, complexity, slow setup, need for training, performance issues, backup problems, security risks, license fees, limited flexibility, and vendor lock-in. You can download a PDF for detailed explanation of each point.
RDBMS can be complex and not suitable for very large or unstructured data. They also need more processing power and trained staff.
Some data models are hard to design and update. They may also lack flexibility when the data structure changes.
Too much data can slow down the system and cause confusion. Storing and managing it also costs money and effort.
Database transactions can slow down performance if not handled properly. They also need strong control to avoid data errors.
A key disadvantage is the high cost of hardware, software, and licenses. Also, it takes time to set up and maintain.
Manual databases are hard to manage, take more time, and are prone to human errors. They also don’t support fast data searching or reporting.
DBMS can be helpful but may be costly and complex for small businesses. They might need simpler solutions based on their needs.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks





