Types and Classification of a Computer (Size and Capacity Based)
Published: 5 Feb 2024
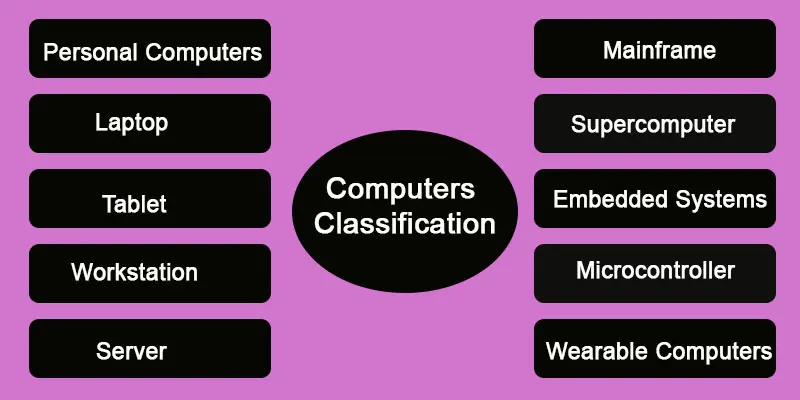
Types of Computer
Computers come in different types, each made for specific things. Knowing the various types of computers is important, whether you need one for personal use, work, school, Business, education, or special tasks.
From desktops and laptops to servers, mainframes, personal computers, tablets, workstations, supercomputers, microcontrollers, and Wearable Computers, each type of computer serves a unique purpose, and understanding their classification can help you make informed technology decisions.
Types and Classification of Computers According to Size
Computers come in different sizes. Small computers are called “microcomputers” or “personal computers.” Medium-sized computers, known as “minicomputers,” handle more complex jobs for businesses or universities. Large computers, called “mainframes,” are powerful machines big organizations use for handling huge amounts of data and complex calculations. Each size of computer has its strengths and is used for different kinds of work.
Personal Computer (PC)
These are the heroes of every day. Your laptop or desktop is used daily at home. It performs daily tasks such as watching videos, creating documents, and browsing the Internet. This is the most common type of computer used by individuals for personal tasks such as browsing, email, and office applications.
Laptop
Laptops are like mini PCs. A portable variant of the personal computer, ideal for users who need to work on the go and handle and manage the amount of data. They’re a type of personal computer designed for mobility.
Tablet
Tablets are lightweight, easy to carry, and enjoyable for browsing, reading, or casual gaming. We make the picture of a magic slate. Touchscreen devices are designed for entertainment, web browsing, and lightweight productivity tasks.
Workstation
Workstations are powerful computers specially made for graphics design, video editing, and scientific simulations. High-performance computers have scientific, technical, and design uses.
Server
Servers are like friendly waiters in a restaurant. They serve information to other computers or devices. Computers are designed to manage network resources, and websites, emails, and files are served up by servers. Servers also provide services to store data for client computers.
Mainframe
Organizations use large and powerful computers for heavy-duty data processing and enterprise-level applications. They manage and process data for large organizations, like the central command center for big companies.
Supercomputer
These are like the superheroes of the computer world. They can handle various calculations at incredibly high speeds, have exceptional processing power, and are used for complex scientific simulations and calculations.
Embedded Systems
These are like hidden gems. They’re tucked away inside other devices, running specific functions. Computers are integrated into other devices, such as cars, appliances, and medical supplies, to perform particular functions.
The microcontroller is called a micrometer.
A microcontroller is a small circuit comprising memory, programmable peripherals for input and output units, and a central CPU unit. It is often used in embedded systems for specific control-oriented tasks, such as appliances, automotive control systems, or even simple electronics projects. Small, low-cost computers control devices and systems in various applications.
Wearable Computers
A wearable computer is small. Devices such as smartwatches and fitness trackers are worn on the body and provide various functionalities. They are designed to be lightweight, portable, and integrated seamlessly into daily life.
Classification of Computers Based on Their Capacity
The following types of computer categories are analog, digital, and hybrid.
Analog Computers
Unlike digital computers, which employ discrete binary codes (0s and 1s), analog computers process information using continuous signals. These quantities continuously exist physically, such as electrical voltages, currents, or mechanical moves; how do analog computers represent data? These computers are meant to manipulate these continuous impulses to solve mathematical tasks.
Digital Computers
A digital computer is a versatile electronic device that processes information using discrete binary code represented by 0s and 1s. Digital computers operate with distinct values, allowing for precise calculations and reliable data storage. An important part is a central processing unit (CPU) for carrying out instructions, memory for storing temporary data, and storage media for storing data for an extended period.

Hybrid Computers
Hybrid computers combine digital and analog computing elements to the advantage of each technology. These systems combine discrete and continuous data processing capabilities to handle various jobs.
Conclusion about Types of Computer
Computers come in various types; each has its unique features and purpose. Laptops and computers are powerful machines that perform complex operations. There are ten main kinds of computer-based on-size personal computers: laptops, tablets, workstations, servers, mainframes, supercomputers, embedded systems, microcontrollers, and wearable computers.
FAQS (Frequently Asked Questions)
How can we divide computers into three basic types?
Computers are divided into three primary categories: desktop computers, laptops, and mobile devices such as tablets and smartphones.
Which is not a computer classification?
The option not typically considered a primary computer classification is “Refrigerators.”
How many types of classification of a computer?
There are various ways to classify computers, but the most common classifications are based on size. The primary types include personal computers, laptops, tablets, workstations, servers, mainframes, supercomputers, embedded systems, microcontrollers, and wearable computers.
Write the definition of a mini computer?
A minicomputer is a moderate-sized computing device that balances larger mainframe computers and smaller personal computers.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks





