What is Virtualization? Examples, Types, History, Benefits, and More.
Published: 3 Jan 2025
What is a Virtualization?
The technique of building a virtual version of a computer or operating system rather than using a real one is known as virtualization. Allowing multiple virtual computers—also referred to as virtual machines—to run on a single physical computer boosts productivity and adaptability. Like any other computer, each virtual machine can run its own operating system and apps even if it shares the same hardware. This helps save space, reduce costs, and improve resource usage.
Examples of Virtualization
- Running multiple operating systems on one computer, like Windows and Linux.
- Virtual desktops allow different users to access separate workspaces on one machine.
- Cloud services like Google Drive use virtualization to store data on remote servers.
- Virtual machines let you test software on different systems without extra hardware.
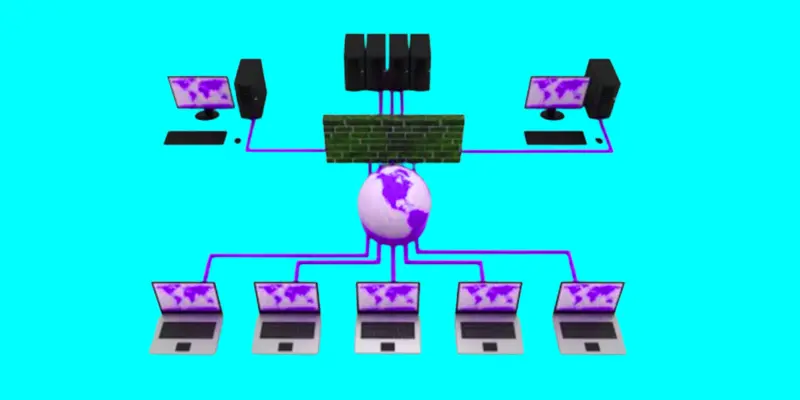
How does Virtualization work?
Virtual machines (VMs) are created and managed by specialized software known as a hypervisor, which is how virtualization operates.
- Installing a Hypervisor on Hardware: The hypervisor regulates the sharing of resources like CPU, memory, and storage between the virtual machines and the actual hardware.
- Creates virtual machines (VMs): It divides the physical computer into separate virtual computers, each with its own operating system and programs.
- Shares resources: The hypervisor allocates parts of the physical machine’s resources (like memory or processor power) to each VM so they can run independently.
- Runs multiple systems: Each VM thinks it’s running on its own computer, even though it’s sharing the same physical machine with others.
History of Virtualization
The history of virtualization began in the 1960s and has evolved over time:
- 1960s – Early Ideas: Virtualization started with the development of mainframe computers. Companies like IBM created systems that could share resources between multiple users, allowing multiple tasks to run on one computer at the same time.
- 1970s – IBM VM/370: IBM’s VM/370 system made it possible for several virtual machines to operate on a single mainframe. This was a big step toward modern virtualization.
- 1990s – Growth in Servers: Virtualization started to spread beyond mainframes, especially in server environments. Companies wanted to make better use of expensive hardware by running several operating systems on one physical machine.
- 2000s – Virtualization for Everyone: In the 2000s, companies like VMware and Microsoft made virtualization software widely available, allowing businesses to run virtual machines on regular servers, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- 2010s – Cloud Computing: With the rise of cloud computing, virtualization became essential for running large data centers. Virtual machines were used to provide on-demand services, like cloud storage and computing power.
- Present Day: Virtualization is now standard practice for both businesses and personal use, with technologies like virtual desktops, cloud services, and containerization (smaller, more efficient virtual environments).

Virtualization Types
In this section, we’ll explore different types of virtualization, each offering unique benefits to improve overall performance and reduce costs.
Hardware Virtualization
The practice of building virtual computers on a physical computer so that several operating systems can operate on the same hardware is known as hardware virtualization. Every virtual machine has its own memory and CPU and functions similarly to a standalone computer. This helps make better use of hardware, improving efficiency and saving costs.
Operating System Virtualization
Multiple operating system versions can operate on a same physical machine thanks to operating system virtualization. It creates separate virtual environments so different applications or tasks can run independently, even if they require different OS versions. This helps test software or run different programs without needing extra hardware.
Desktop Virtualization
Desktop virtualization lets users access their desktop environment from any device, anywhere. The desktop is stored on a remote server, not the user’s local machine, allowing for easier management and security. This way, users can work from different locations without needing to carry their physical computer.
Network Virtualization
Several physical networks are combined into a single virtual network using network virtualization. It simplifies network management by allowing resources to be allocated more efficiently and securely. This way, businesses can improve performance, reduce costs, and easily scale their network as needed.
Storage Virtualization
Several storage devices are combined into a single virtual pool using storage virtualization. Because all of the storage appears as a single unit, data management is made easier. It helps businesses improve efficiency, simplify data management, and better utilize their storage resources.
Application Virtualization
Application virtualization allows software applications to run on a virtual environment without being installed directly on a computer. Users can access and use the applications from any device, making it easier to manage and update software. This helps save time and resources, as applications can be run remotely.
Server Virtualization
Using server virtualization, a real server is split up into multiple virtual servers, each of which has its own operating system and suite of apps. This lowers expenses, increases efficiency, and makes the best use of hardware resources. Businesses can run several tasks on one server, saving space and energy.
Data Virtualization
Data virtualization allows data from different sources to be accessed and managed as if it’s all in one place, without moving it. This makes it easier to work with data from various systems without needing to store it all together. It helps businesses make faster decisions by providing real-time access to information.
Memory Virtualization
By establishing a virtual memory space, memory virtualization enables a computer to utilize more memory than is physically available. It helps applications run smoothly, even if there isn’t enough RAM. This improves performance and allows the system to handle larger workloads without slowing down.
Cloud Virtualization
Cloud virtualization uses virtual machines and resources in the cloud to provide on-demand services like storage and computing power. It allows businesses to access these resources over the internet without needing to own physical hardware. This improves flexibility and lowers costs by making it simpler to scale up or down in response to needs.
Benefits of Virtualization
- Cost Savings: By running several virtual machines on a single physical computer, virtualization eliminates the need to purchase additional hardware. This helps save money on servers, power, and space.
- Efficiency: Virtualization lets you use your computer’s resources more effectively. It helps make better use of CPU, memory, and storage by running multiple systems at once without wasting resources.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Virtualization makes it easy to create, move, or change virtual machines as needed. You can quickly add new virtual systems or change existing ones, allowing for easier management and growth as your needs change.
Virtualization versus Containerization
| Virtualization | Containerization |
| Creates virtual machines with their own OS. | Runs applications in isolated environments. |
| Uses more resources since each VM runs its own OS. | Uses fewer resources as containers share the host OS. |
| More complex issues require a separate OS for each VM. | Simpler containers share the same OS kernel. |
| Can be slower due to running full operating systems. | Faster, as containers are lighter and share the OS. |
| Strong isolation between virtual machines. | Good isolation, but containers share the host OS kernel. |
| Best for running multiple operating systems on one machine. | Ideal for running lightweight, microservices or apps in a consistent environment. |
| VMware, Hyper-V | Docker, Kubernetes. |
Conclusion about Virtualization
Several systems can operate on a single piece of hardware thanks to the potent technology known as virtualization. It helps businesses and individuals save costs, use resources efficiently, and manage systems more flexibly. By creating virtual machines or environments, virtualization enables better use of physical devices, simplifies IT management, and supports cloud computing, making it an essential part of modern technology.
FAQS – Virtualization it
What does virtualization mean?
Virtualization means creating virtual versions of hardware, like computers or servers, on a single physical machine. It lets multiple systems run independently on the same hardware, saving costs and making IT management more flexible and efficient.
What is virtualization in IT?
Virtualization in IT is creating virtual versions of computers, servers, or storage on a single physical machine. This allows multiple systems to run on one device, improving efficiency and saving costs.
What is a virtualization server?
A physical server that houses several virtual machines (VMs) is called a virtualization server. By doing numerous activities on a single computer, each virtual machine (VM) helps to optimize the server’s resources by running its own operating system and applications.
VMware: What is virtualization?
Multiple operating systems can run on the same physical device thanks to VMware’s virtualization technology, which builds virtual copies of desktops, servers, and PCs. This makes better use of resources and makes system management easier for enterprises.
What is virtualization technology?
By creating virtual computers on a physical computer, virtualization technology makes it possible for many systems and apps to operate on the same hardware. This technology is used for server management, storage, and more, saving costs and enhancing flexibility.
What is virtualization in the cloud?
In cloud computing, virtualization allows virtual machines, storage, and resources to be delivered over the internet. Cloud virtualization lets users access services on demand without needing their own hardware, making it flexible and cost-effective.
What is virtualization in a computer?
Virtualization in a computer creates virtual environments within the same device, such as virtual machines with separate operating systems. This allows one computer to run multiple “mini-computers,” improving resource use and flexibility.
What is virtualization in computer networks?
Virtualization in computer networks combines multiple physical networks or devices into a single virtual network. This simplifies network management, improves efficiency, and allows for faster deployment of resources.

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks

- Be Respectful
- Stay Relevant
- Stay Positive
- True Feedback
- Encourage Discussion
- Avoid Spamming
- No Fake News
- Don't Copy-Paste
- No Personal Attacks